


Syntax – WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, 10) WebElement element = wait.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(By.id(“ID”)))
#Webdrive implicit vs explicit wait driver
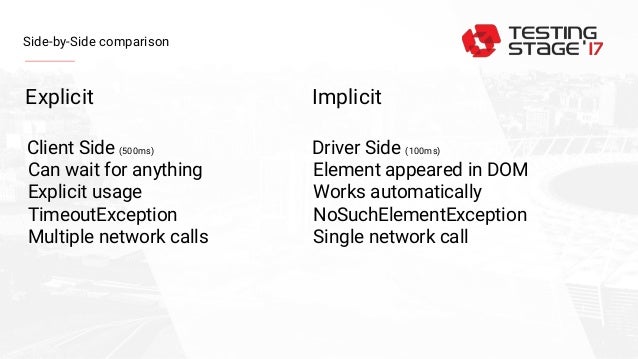
Explicit wait is used to tell the Web Driver to wait for certain conditions (Expected Conditions) before proceeding with executing the code.Example- WebDriver driver= new FirefoxDriver() ĭriver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS) Time – It is an integer value Second parameter is the time measurement in terms of SECONDS, MINUTES, MILLISECOND, MICROSECONDS, NANOSECONDS, DAYS, HOURS, etc. Syntax – driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(time, TimeUnit.SECONDS) If still element is not found, NoSuchElementFound Exception will be thrown. So after waiting for a specific time, it will try finding the element. We are telling WebDriver to wait for a specific amount of time before it can expect the element to be visible after loading. Selenium webDriver provides three types of waits : When a page is loaded by the browser ,the elements which we want to interact with may load at different time intervals due to usage Ajax and Javascript in the application so we have to provide some waits for performing an action on a particular element. We can handle these anticipated timing problems by synchronising our test to ensure that Selenium WebDriver waits until the application is ready before performing a certain action. Selenium- Maven Integration with Selenium Selenium- Read and Write csv file in Selenium Selenium- Read & write excel file using Apache POI Selenium- Database Testing using Selenium Selenium- Read excel file using Fillo API Selenium- difference b/w driver.get() & driver.navigate() Selenium- Difference b/w driver.close() & driver.quit() Selenium- Exceptions and Exception Handling
#Webdrive implicit vs explicit wait code
Difference b/w Selenium IDE, RC & WebDriverīackground when user execute selenium code


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
